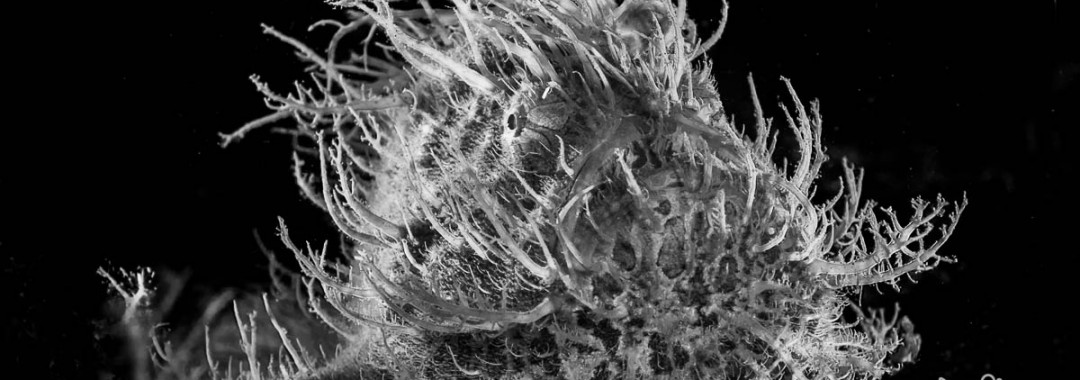
This Week’s Tip: How to Photograph ‘Frogfish’
Frogfish or Anglerfish are a favorite subject of many photographers, because like nudibranchs they usually don’t move much, although hairy frogfishes tend to be more active than other species. They’re also not shy, so they can be shot from very close distance.
The best lenses to use are macro lenses such as 60mm, 100mm, or 105mm for DSLR’s, (nowadays with different cameras like mirrorless & micro 4/3 etc. the lenses vary a lot, I use a 90mm at the moment on a SONY A7R2). For shooting super-macro images of tiny juveniles, eyes or the lures, use close-up diopters or teleconverters.
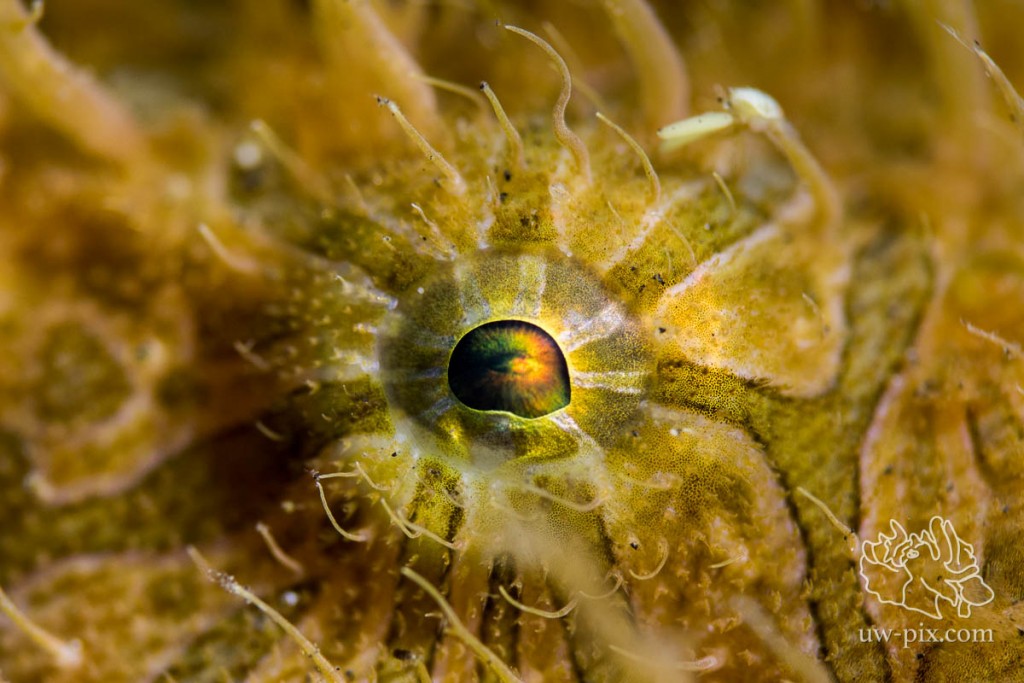

Hairy frogfish (Antennarius striatus) eye – Canon 7D Mark II, 60mm, Nauticam SMC, f5.6, 1/160sec, ISO 160, 1x SOLA 4000, 1x SOLA 2100
For shooting CFWA (close-focus-wide-angle) of giant frogfish, fisheye lenses are the preferred choice, for smaller subjects we can combine the fisheye lens with a teleconverter. Try to get as low as possible and shoot slightly upwards to isolate the fish clearly against the blue water background.
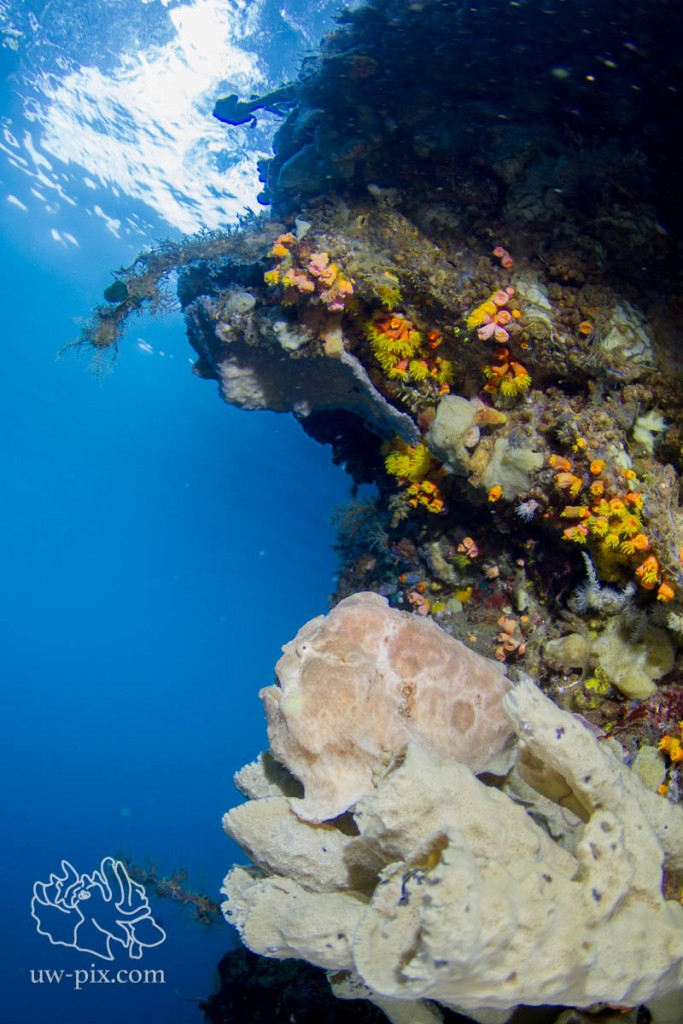

Giant frogfish (Antennarius commerson) sitting on a sponge at the mini-wall @ Nudifalls – shot upwards into the water column to get a blue background – Canon 7D, Tokina 10-17 @ 10mm, f3.5, 1/80sec, ISO200, 2xL&M SunRay 2000 LED lights
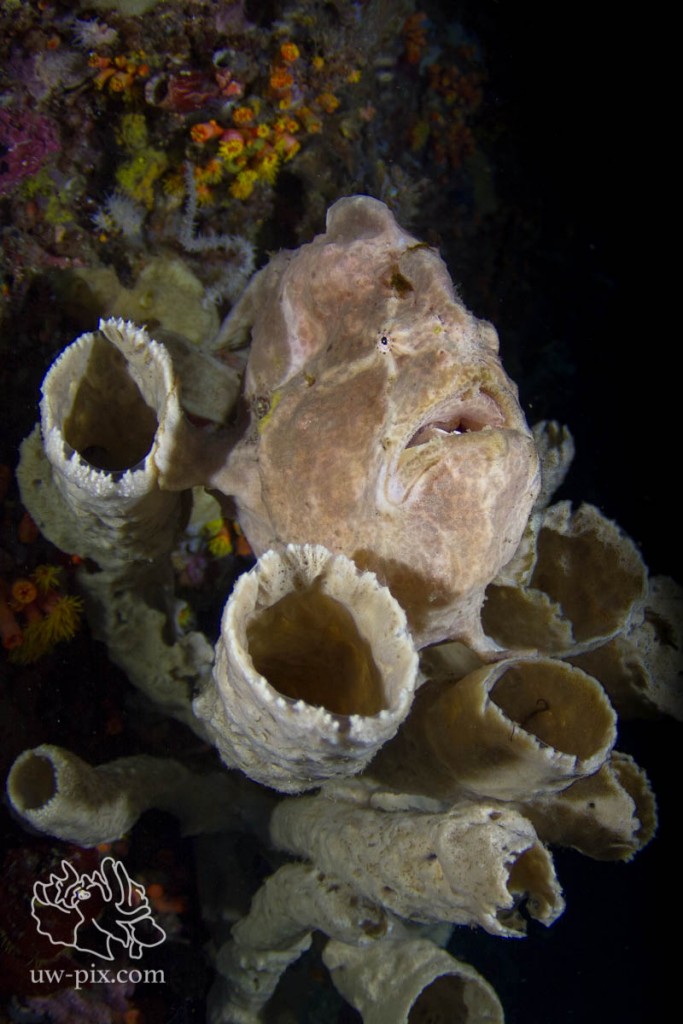

The same giant frogfish (Antennarius commerson) on the same sponge, this time shot downwards in the water column to get a black background – Canon 7D, Tokina 10-17 @ 10mm, f3.5, 1/250sec, ISO200, 2xL&M SunRay 2000 LED lights
To show how well they camouflage, it sometimes can be nice to back off a bit and not fill the frame with the frogfish.
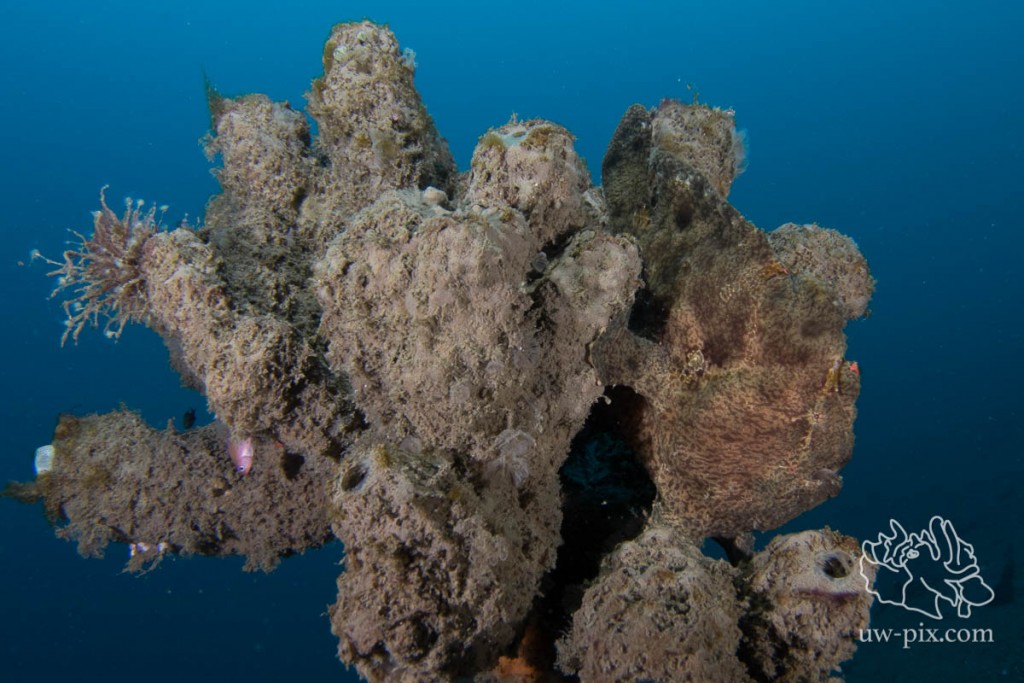

Giant frogfish (Antennarius commerson) on a sponge – Canon 7D Mark II, Tokina 10-17, Kenko 1.4 TC @14mm, f8, 1/125sec, ISO640, 2xSOLA 4000
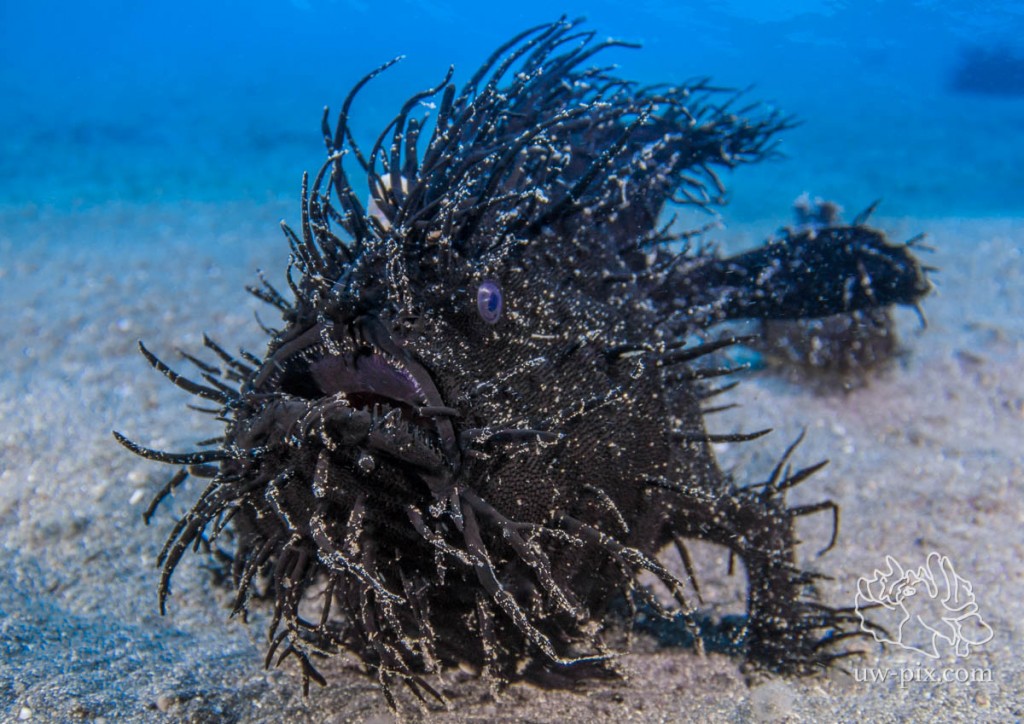

Getting really close is key when shooting CFWA, using a mini dome is recommended. Black hairy frogfish (Antennarius striatus) very close to the port – Canon 7D Mark II, Tokina 10-17, Kenko 1.4 TC @14mm, f10, 1/50sec, ISO320, 2x i-Torch Venom 50, 2x i-Torch Venom C92
When frogfish are ‘luring’, try to shoot them from the side, to get the lure and the frogfish in focus
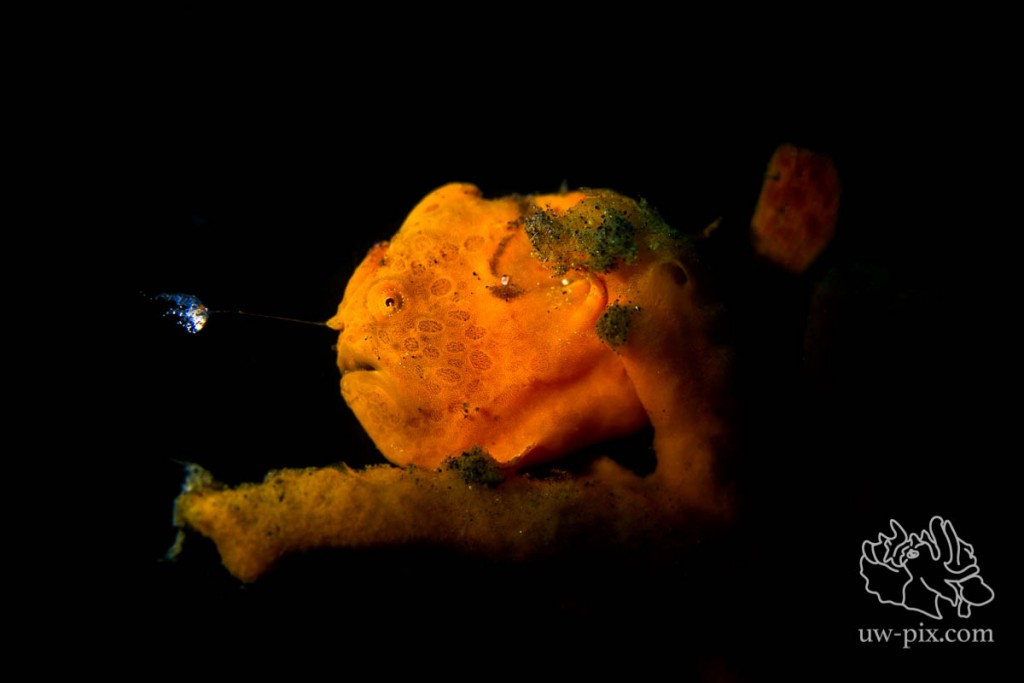

Painted frogfish (Antennarius pictus) fishing with its lure – Canon 7D, 60mmm macro, f5.6, 1/320sec, ISO160, 1xSOLA 1200 on spot
Frogfish also look cool when shooting portraits, it can be nice to fill the frame with the face only (especially when you run into a larger frogfish with a 100/105 (or 90mm 😉 ).
Use a large aperture (low f-number) to get out of focus backgrounds and foregrounds.
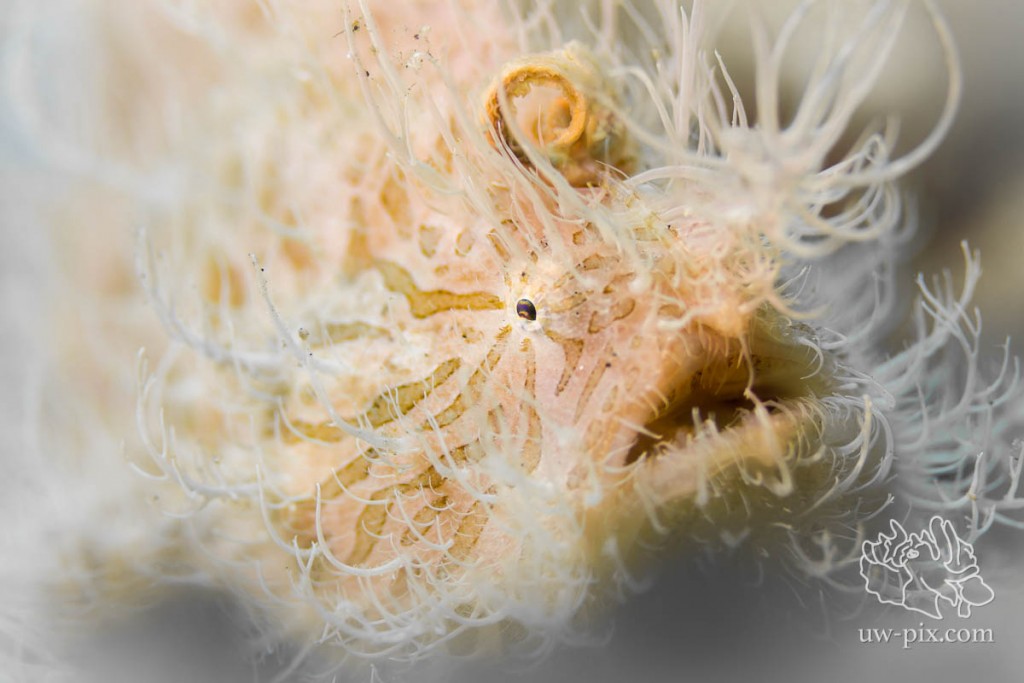

Hairy Frogfish (Antennarius striatus) close-up portrait shot with a large aperture – Canon 7D, 100mm macro, f3.5, 1/800sec, ISO160, 2x L&M SunRay2000 LED lights. This frogfish was just too big for my lens (100mm), so I decided to go for a portrait.
Why can using only one light-source be helpful?
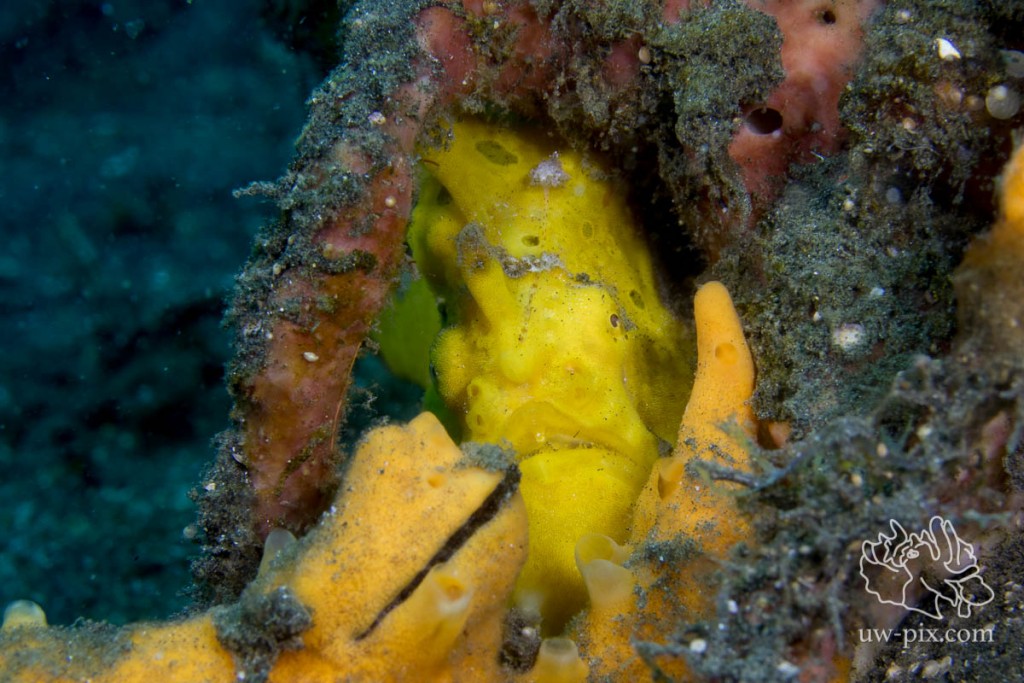

Warty frogfish (Antennarius maculatus) sitting in sponges, 2 lights lighting up the subject, but also the distracting background – Canon 7D Mark II, 60mm macro, f13, 1/60sec, ISO160, 1xSOLA4000, 1xSOLA2100
Using only one light-source will create dramatic shadows and can give us a darker background if we don’t light up all that sand.
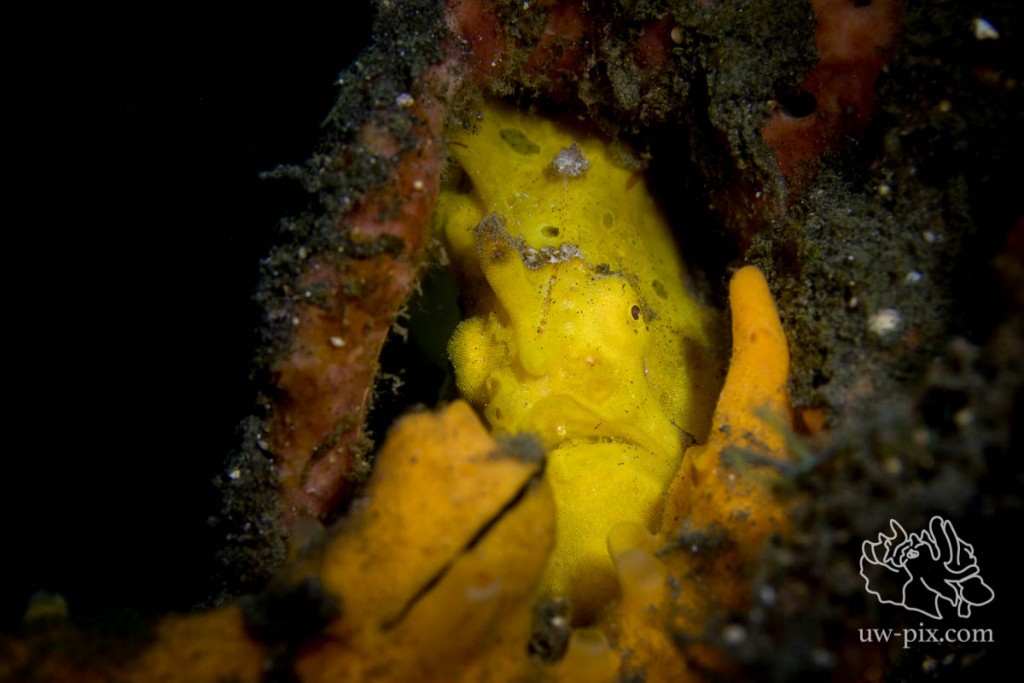

The exact same subject (and exact same camera position), but this time I used only one LED light on spot – Canon 7D Mark II, 60mm macro, f5.6, 1/1000sec, ISO160, 1xSOLA2100 (on spot) – to get a similar result with a strobe, use a snoot.
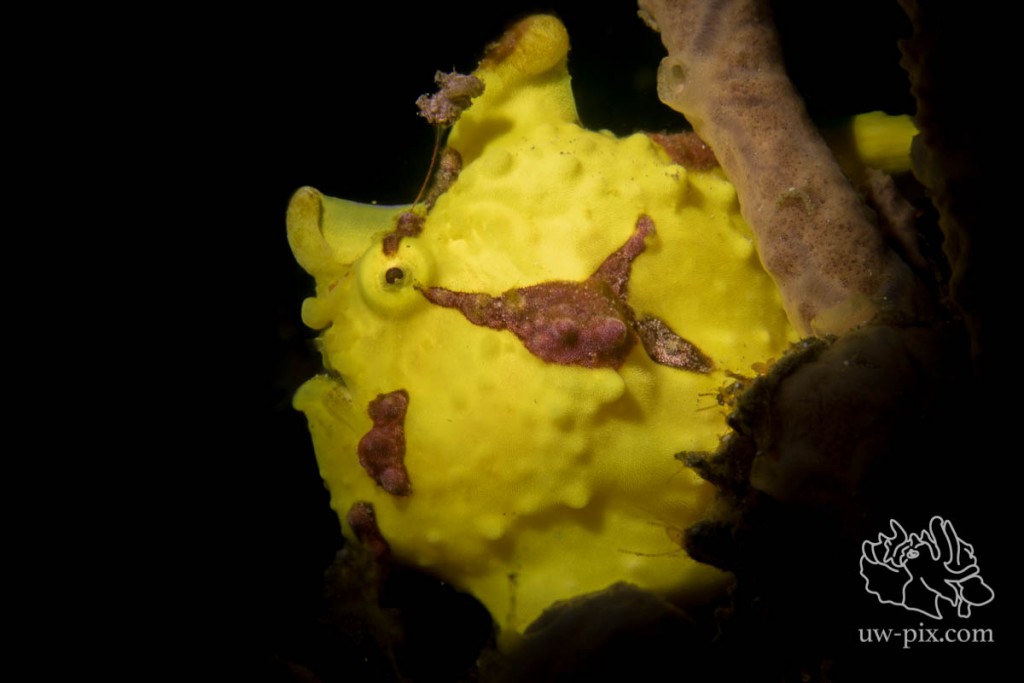

Warty frogfish (Antennarius maculatus) shot with one LED light on spot – Canon 7D Mark II, 60mm macro, f16, 1/60sec, ISO100, 1x Sea Dragon 2100 on spot
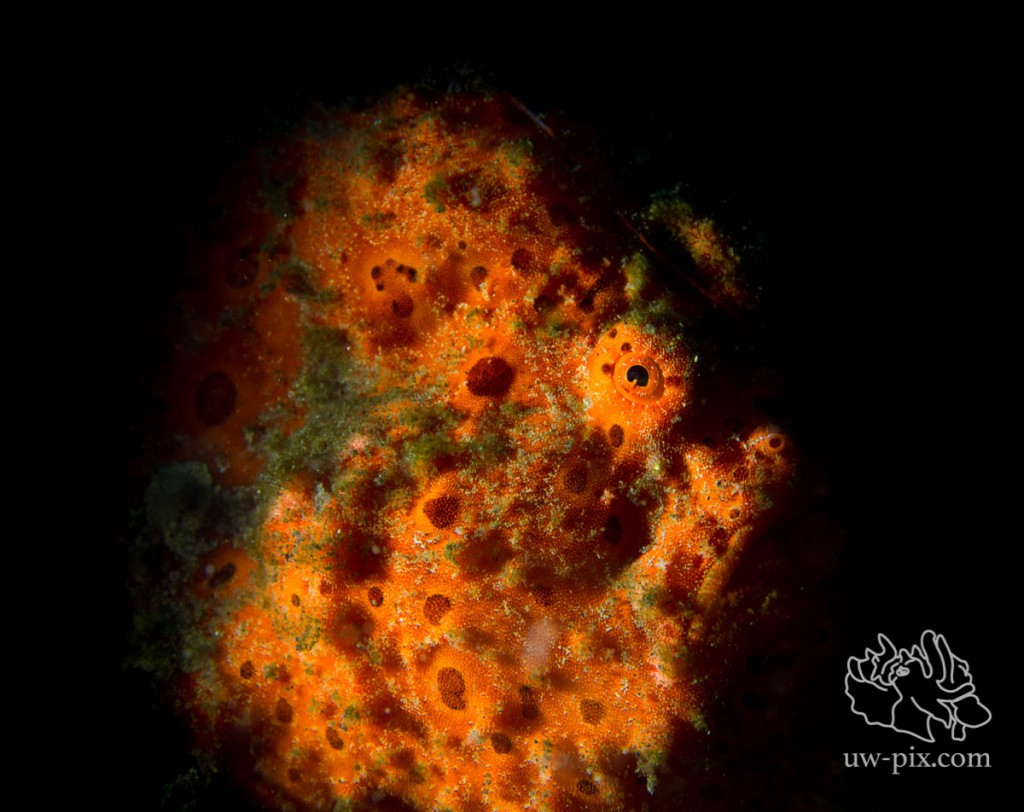
When using a snoot or spot on a LED light, black backgrounds and dramatic shadows are possible – Canon 7D, 60mm macro, f11, 1/125sec, ISO160, 1x SOLA1200 on spot
Always remember that with moving your strobe/light around you’ll get different results as I mentioned here:

For hairy frogfish, backlighting with a LED light or a strobe will make the hairs stand out more. Use one strobe from behind and one from the front to light up the face as well.
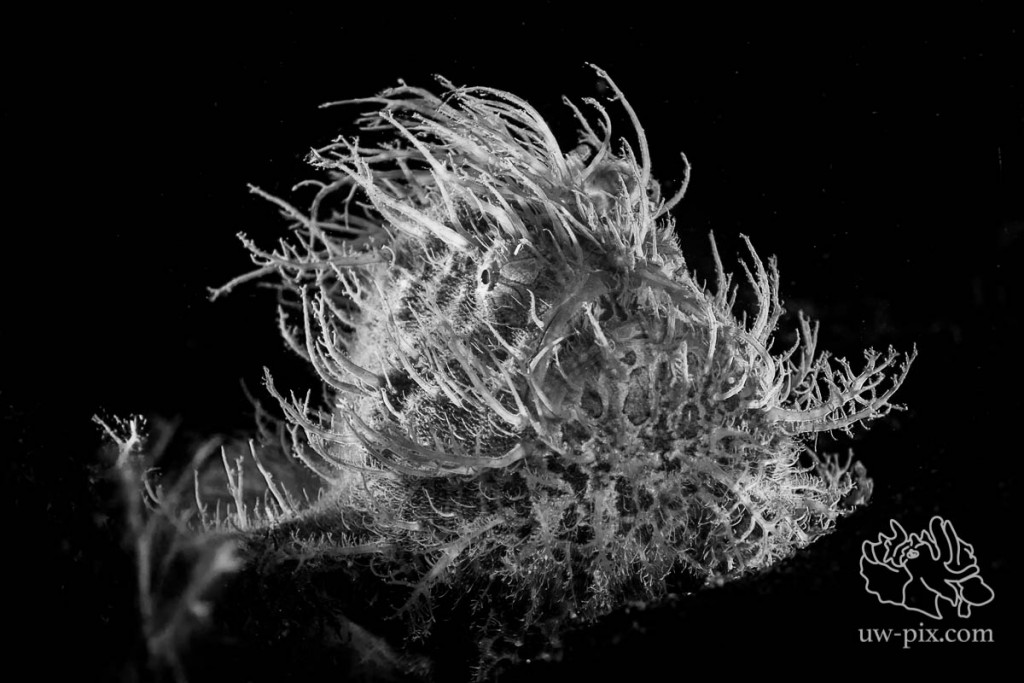

Hairy frogfish (Antennarius striatus) backlit to make the hair stand out more – Canon 7D Mark II, 60mm macro, f11, 1/200sec, ISO160, 2x SOLA 4000 (1xfront, 1xback), 1x SOLA2100(front), 1x F.I.T.2400WSR (back)
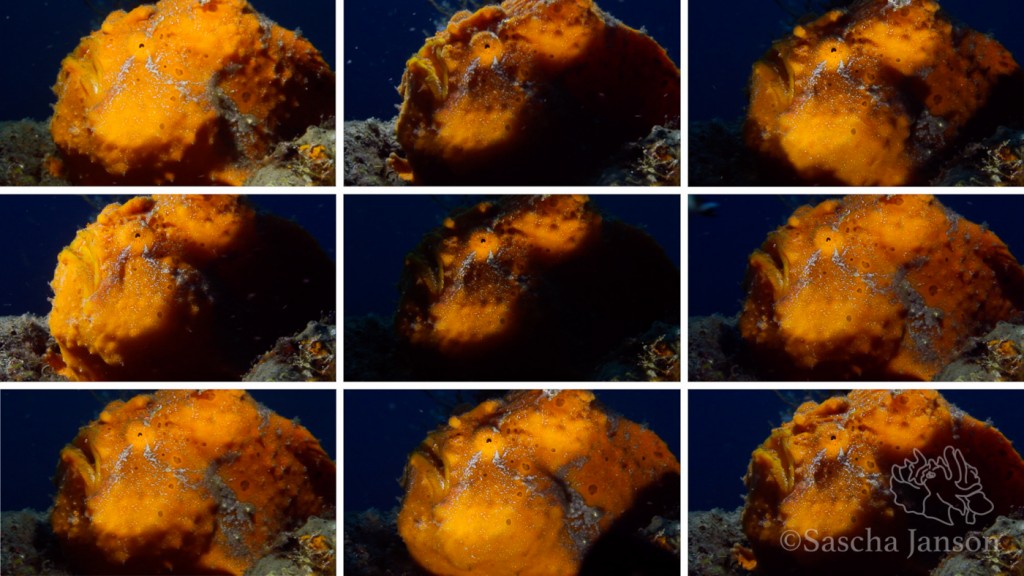
To get behavior shots like yawning, you have to be patient (and of course lucky), frogfish often open their mouths a little bit only just seconds before the real yawn, so try to be ready for the shot and have your settings right. Take a couple test shots and when you have your exposure right, then wait. Of course don’t wait too long if there are other divers waiting for their turn to see/photograph the frogfish.
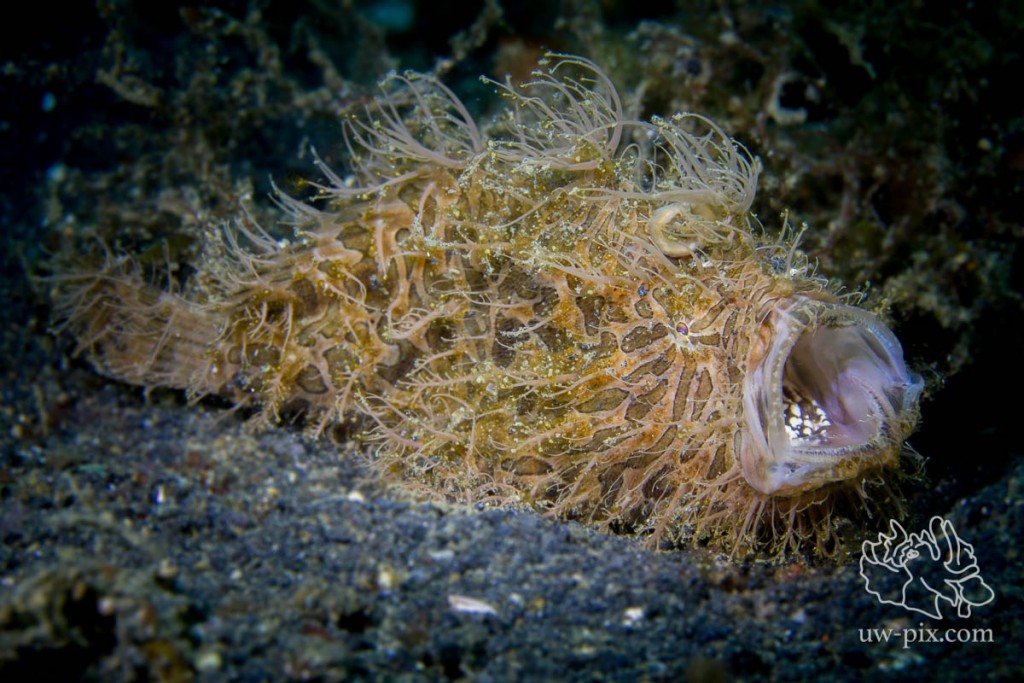

Hairy frogfish (Antennarius striatus) yawning – Canon 7D, 60mm macro
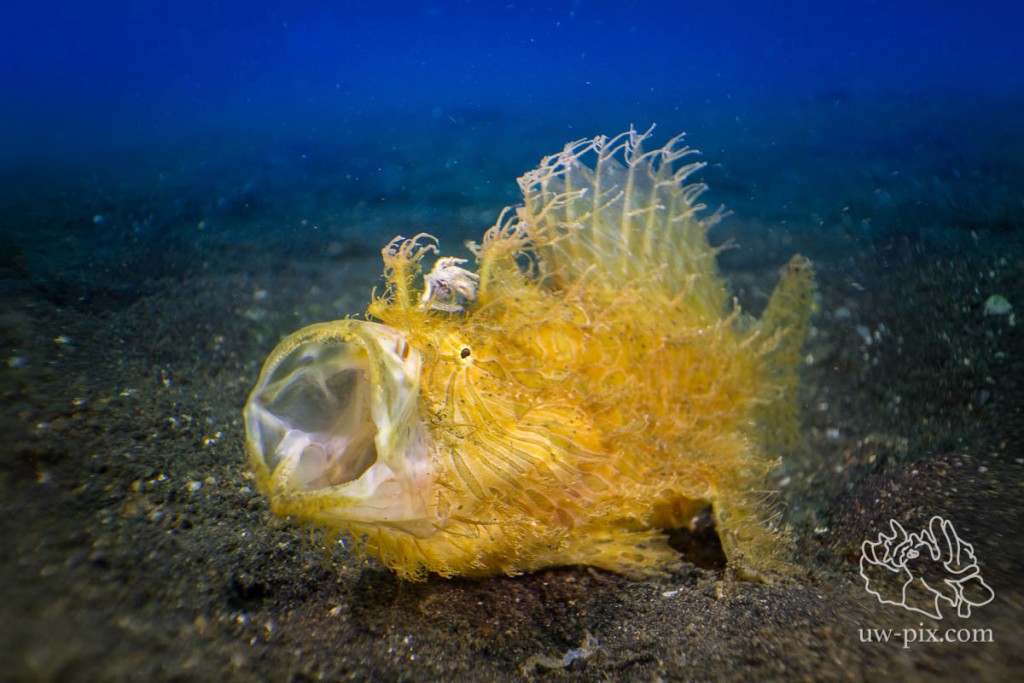

CFWA Hairy frogfish (Antennarius striatus) yawning – Canon 7D, 60mm macro, CFWA wet-lens (that’s why there are blurry edges), f5.6, 1/200sec, ISO160, 2x SOLA 4000
Even if frogfish usually don’t move much and seem to be relaxed, never harass them (the same goes for every creature underwater). We often see frogfishes in the same spots for many months, but if they’re harassed, they move away and future divers cannot get a glimpse of the weird and wonderful world of frogfishes.